What Is The Process Within Continual Service Improvement?
Definition of ITIL Continual Service Improvement (CSI)
ITIL Continual Service Improvement (CSI) is the fifth and final phase of ITIL Service Lifecycle nether ITIL's IT Service Management Framework (ITSM). It aims to deal with measures to be adopted to better the service quality by learning from past successes and failures. Continual Service Comeback also aligns and realigns IT Services to the irresolute business concern requirements by identifying and implementing changes for improvements. For doing this, it takes the like approach described in Deming Bike (PDSA Cycle). The ITIL Continual Service Improvement (CSI) describes the best practices for achieving incremental and large-scale improvements in services quality, operational efficiency, and business continuity. It effectively describes and utilizes the concept of Key Performance Indicator (KPI), which is a metrics-driven procedure, for reviewing, evaluating, and benchmarking functioning of services.[1]
The CSI Practice relies upon v major guiding principles defined in the CSI book:
- The CSI Approach
- 7 Pace Improvement Process
- The Deming Cycle
- Professor Kotter's Eight Steps for Successful Transformation
- Cognition Management
The effigy beneath illustrates the It Infrastructure Library (ITIL) Continual Service Improvement (CSI) seven-pace process. The private steps overlayed by the more general Deming (plan-practice-check-human activity) Bike. It also shows how the cycle fits into the Data-to-Information-to-Knowledge-to-Wisdom (DIKW) structure of knowledge management
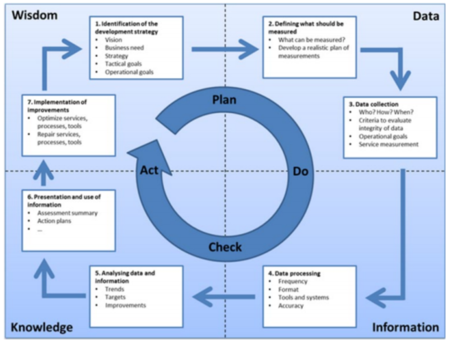
source: Geant.Org
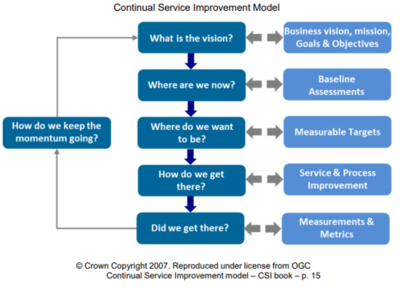
ITIL Continual Service Improvement (CSI) Approach[2]
The CSI Model follows a half dozen-step approach for reviewing, evaluation, planning, and implementing the Improvement procedure. These approaches are nothing but some pre-defined questions, for which the CSI procedure tries to find answers.
- Step one – What Is The Vision?: CSI is all about the Concern, so when looking at the CSI Model the first step is to conspicuously understand the Business vision, strategy, goals and objectives. It is also important to sympathize ITs strategy, goals and objectives, and to ensure that they back up the Businesses.
- Footstep 2 – Where Are We Now?: In guild to be able to place if you take improved, information technology is important to know where you lot started from. Answering this question is about performing an initial cess, or measurements, in gild to create a baseline upon which improvement effort success can be measured. Cess can exist done on availability and/or performance of It Services. Assessments can besides be washed around processes such equally a procedure maturity assessment. If you don't have whatever basic measurements or metrics today you may demand to offset collecting these for iii to six months and then get understanding on a baseline number.
- Step 3 – Where Do Nosotros Desire To Be?: Prepare realistic targets for the improvement initiative. This may require setting short-term, mid-term and long-term targets. Targets can be set up for availability measures for IT Services or a new maturity level for processes. Keep in mind that setting targets should be based on business requirements, and non on business wishes. If a customer says they want 99.999% availability, be certain that this is what they really need to back up the desired business organization outcomes they demand to reach. Also remember that for procedure maturity, the cardinal is once more to sympathise the value of a process to the business. Non all processes are equal and some processes will deliver more than value to the business than others. The target should not exist to have all processes at a level five maturity. You may discover that being at a level three is all you demand to deliver value. Create your Measurement Framework of Key Functioning Indicators so that after on you can measure if you have achieved your targets.
- Step 4 – How Do We Get There?: This is the process improvement projects that are identified, agreed on and funded. Keep in mind that Senior Management oftentimes does not accept the luxury of long projects. They are interested in getting quick improvements, and so don't overlook the quick wins that can be implemented around It Services and/or processes
- Footstep 5 – Did We Get There?: Using the Cardinal Performance Indictors defined in Step three, go on to monitor, measure and written report on your achievements. *Step vi – How Practise We Proceed The Momentum Going?: Market your successes to Senior Management likewise every bit the rest of the arrangement. It is of import to employ successes to gain more purchase-in for boosted comeback initiatives.
The Seven Step Improvement Process[3]
The focus of Continual Service Comeback is on service improvement to support business processes. To achieve this, Continual Service Comeback uses a seven-step process plan for comeback which is crucial for CSI and other stages in the ITIL lifecycle. The master purpose of this process is to define and manage the steps required to identify, define, gather, process, analyze, present and implement the improvements which have been made over a menstruation of time. The seven step improvement process is essential in supporting CSI and operates across the unabridged service lifecycle. Information technology focuses on identifying the comeback opportunities, not merely for processes and services, just for all the disciplines implemented as a part of the It Service Lifecycle.
Scope of the Seven-Step Comeback Procedure
The scope of the CSI seven-step improvement process contains the post-obit areas:
- The vii-step comeback process includes analysis of the functioning and actual capabilities of the services and processes throughout the lifecycle, partners, and applied science.
- It includes continuously aligning the portfolio of IT services of the organization to the present and future business organisation requirements.
- It makes the best utilize of whatever the engineering that the organization possesses and tries to acquire and utilize new technology when a business instance demands information technology.
- To determine the capabilities of the personnel in the enterprise and to enquire if the right people with the relevant skills are working in advisable positions.
Value of the Vii-Footstep Improvement Process
With the aid of aforementioned 7-footstep Comeback processes in ITIL Continuous Service improvement, current and futurity business organization requirements are met past constant monitoring and analyzing service delivery. Indeed, it besides enables repetitive cess of the present situation confronting business requirements and identifies the opportunities available for improving the provision of service to the customers.
Principles and Basic Concepts of the Seven-Footstep Improvement Process
Continual Service Improvements should eye on increasing efficiency, maximizing the effectiveness, reducing the price of service, and underlying IT service direction. And the only way to accomplish the chore is to ensure that the improvement opportunities are identified throughout the service lifecycle.
- The service providers operate in a very competitive market and they need to assess their services against the expectations in the market place persistently.
- New delivery mechanisms such as cloud computing can increase the efficiency of the service and need to exist considered for implementation.
- The service provided must be compared to the nowadays market offerings to ensure that the service adds actual business value to the clients, so that the service provider remains competitive.
- The services must exist regularly reviewed to continue up with the latest technological advances to ensure that the services they are delivering are the nigh efficient.
Stages in the Seven-Pace Improvement Process
The below mentioned vii steps institute what is known as a cognition screw. The knowledge gathered from one level becomes the input to the other level. It moves from operational management to tactical management and finally strategic management. Feedback from any phase of the service lifecycle can exist used to identify comeback opportunities for any other phase of the lifecycle. The stages in the vii stride improvement process are listed below:
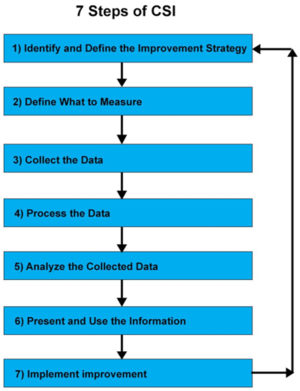
The vii Steps in the CSI Process
- Identify the approach for improvement: Prior to implementing an improvement strategy, it's necessary to understand the necessity for continuous improvement. We must take into account the last goals we have gear up for the business organization and encounter how the IT organization tin assist in achieving those targets through continuous improvements. Whilst accomplishing this, consider future and nowadays plans as well.
- Define what should be measured: A comparison should be made amid what we can ideally measure out and what we can actually measure. Gaps should be identified and a realistic measurement plan should be incorporated to back up the strategy for improvement.
- Collect the essential information: Data is gathered through persistent monitoring. The process of monitoring can be done either through manually or applied science can exist utilized to the fullest to automate the entire procedure and simplify it.
- Process the data: One time the information is collected through continuous monitoring, it is then converted into the form required by the audience. This can be considered as a conversion of metrics into Key Performance Indicator (KPI) results and change the available data into information.
- Analyze the information and data: The multiple sources of information are combined to transform the data into noesis, which is further analyzed to detect the gaps and their bear on on the overall business. The information is further evaluated considering all the relevant internal and external factors. It also helps to answer questions regarding something that is good or bad and is it expected and in line with the targets.
- Proper presentation and utilization of information: The information which is gathered and analyzed needs to exist presented in a proper fashion with the right amount of detail so that the information is comprehensible and provides the required amount of detail to back up informed decision making.
- Implement the improvements: A change implemented with continuous improvement sets a new baseline for the unabridged process. The knowledge obtained should be combined with the previous feel and are used to make informed decisions and necessary improvements. The improvements which are made must focus on optimizing and correcting the services, processes, and tools.
The 7 stride improvement procedure is a vital process of CSI and thus identifies the opportunities available for improving services, tools, processes, etc. The procedure initiates service measurement, service reporting, and improvement. This helps to define the service baseline and processes, metrics, KPIs, critical success factors, and cosmetic measures are taken to identify and better the gaps in the Information technology service management. ITIL CSI desires a commitment from the people working throughout the service lifecycle. It requires enduring attention to monitoring, analyzing, a well thought program, and reporting results aiming towards improvement.
The Deming (PDCA) Cycle
The integration of the PDCA wheel and the seven-stride improvement procedure is as follows:
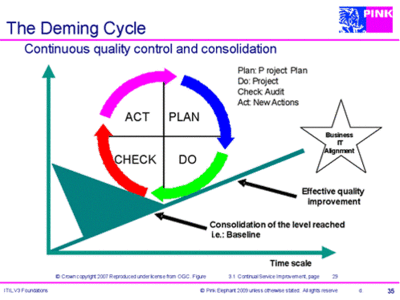
- Program
- 1. Identify the strategy for improvement
- 2. Ascertain what you will measure
- Exercise
- three. Get together the data
- 4. Process the data
- Check
- 5. Analyse the information and data
- half dozen. Nowadays and use the information
- Act
- 7. Implement improvement.
The goal in using the Deming cycle or PDCA bike is steady, ongoing improvement. Information technology is a fundamental tenet of Continual Service Improvement (CSI). For the awarding of CSI to services and service management processes. At implementation all 4 stages of the PDDCA cycle are used. With ongoing improvement, CSI draws check and act stages to monitor, mensurate, review and implement initiatives. PDCA should be repeated multiple times to implement Continual Service Improvement (CSI). Treatment of cultural change is required to implement CSI for improvement. Information technology should be noted that the PDCA cycle is a fundamental part of many quality standards including ISO/IEC 20000.
Knowledge Direction
Knowledge management roles are created to facilitate the continual service improvement (CSI) of procedures, metrics, policies, and documentation. First, there are those that contribute articles. To build a knowledge repository, solutions articles are a must. Generally, when technicians resolve a ticket, they transcribe the steps they took as an article. Any subject thing adept or finish user in the organization can create solution articles.
One time articles are submitted, the appropriate experts review and approve the articles. Upon approval, the knowledge manager publishes the article in the noesis base of operations. The part of these subject thing experts is to review and approve articles to maintain high quality solutions articles in the knowledge base.
The cognition director is a procedure owner with a deep agreement of cognition management practices. The knowledge manager makes certain that the process of collecting, reviewing, approving, and grouping solution articles in the knowledge base is performed effectively.
For instance: A user raises a request in the service desk for information on how to remotely configure a VPN from home. If a knowledge commodity on VPN configuration is already available in the noesis base, the user tin follow the steps in the commodity and avoid raising a ticket altogether. The post-obit are the roles involved in the life bicycle of a knowledge article.
- Commodity contributor: This can be anyone in the service desk-bound, including a technician or a subject thing expert. In this scenario, if a technician notices that many users request the same information on VPN configuration, the technician can write an article on VPN configuration and submit information technology for review.
- Subject area matter expert (SME): Field of study affair experts are those that have expertise and knowledge in their specific areas or departments. An SME will review and amend the submitted article every bit needed. If the commodity submitted meets the standards in terms of technical accuracy, language, and relevance, information technology will exist canonical. If non, information technology is rejected.
- Knowledge director: The cognition director decides in which category approved manufactures volition be published then that users can easily find the manufactures they need. The category "Remote piece of work incidents" is chosen for this article on VPN connections. Once the commodity gets published, it gets tracked periodically to monitor its performance through reports to ensure the relevance of the content is maintained and its quality is improved when possible.
DIKW Model for Knowledge Management
The data, information, knowledge, and wisdom (DIKW) model explains how IT service desk teams tin generate cognition based on their everyday activities. This likewise shows how the transformation of data into information, knowledge, and wisdom occurs along with the relationship between them. This model is also known as the DIKW pyramid or DIKW hierarchy.
- Data: Data is the collection of discreet facts about events in the grade of numbers, characters, and specific or relative values that the organisation can get together. The key activities to exist performed at this phase are:
- Identifying a reliable source to get data
- Archiving and deleting the appropriate information
- Information: This phase is about calculation context to data. The key activities to be performed in this phase are:
- Converting data into data while maintaining information integrity
- Managing data the right style past making it easy for end users to search and use.
- Knowledge: Knowledge is derived from experience. It may involve expertise, values, and judgments of members of the IT service desk team such every bit the cognition managers, field of study matter experts, technicians, or end users. Knowledge created in this stage facilitates smart decision-making.
- Wisdom: Wisdom is the culmination of information, information, and knowledge. It adds value to knowledge management. This value is created though dynamic planning, problem solving, strategic planning, and discernment.
Case scenario: Zylker, an electronics company with over 1,500 employees, is on a recruitment drive. Over the weekend, many new talented individuals were recruited for different teams. But at the start of the week, when the IT team onboarded the starting time employee and assigned them to a team, the file management (FM) awarding failed and none of the teams were able to access any files in the arrangement. While the other teams were almost having an extended weekend, the IT team had to quickly look into the cause of the failure.
For the above state of affairs, let's breakdown the incident and organize information technology into a DIKW hierarchy for knowledge management.
- Data: The IT teams received an incident ticket from the awarding monitoring tool 'TOMCAT_THREADS_EXHAUSTION'
- Data:: The application monitoring tool sheds more light on the ticket with "File server ; Connector port:8332 [Tomcat Busy Threads Pct:100% , Threshold :ninety%] Giving information about the warning helps It teams make sense of information. In this case, the FM server retention usage has been maxed out.
- Noesis: Hither is where the analytic skill set up of the IT team is needed. Afterwards checking the logs of the FM server, the squad constitute multiple parallel requests from the browser client requesting data of all the members of the team where the new employee was just assigned. The team then checked the knowledge manufactures that describe the background processes that occur when a new employee is assigned to a team. They acquire that a complete groundwork refresh occurs for the information of all members of a team when a new employee is assigned to it. The background refresh tries to update information of the team members in browser client enshroud. These requests flooded the FM servers and led to a downtime.
- Wisdom: Wisdom comes from feel and learning what to do when faced with situations like the one described to a higher place.
Every bit an immediate gear up, the service desk-bound squad removed the unnecessary requests from the browser clients and got the service back up and running. As a permanent set up, the team removed the background refresh logic by fetching only the newly added user data and non the unabridged team fellow member list.
The Activities of Continual Service Improvement[four]
- Reviewing direction data and trends to ensure that services are coming together agreed service levels
- Reviewing management data and trends to ensure that the output of ITSM processes are achieving thedesired results
- Conducting maturity assessments against the process activities and roles to highlight areas of improvementor business organisation
- Conducting internal audits verifying compliance
- Conducting external and internal service reviews to identify CSI opportunities
- Reviewing analysed data
- Presenting recommendations to senior management for comeback
- Helping prioritise comeback opportunities
- Leading managing and delivering cross functional and cantankerous divisional improvement projects
- Building effective relationships with the business and It senior managers
- Influencing all levels of direction to ensure that service improvement activities are receiving the necessarysupport and are resourced sufficiently to implement solutions
Objectives and Scope of Continual Service Improvement
The Objectives of Continual Service Comeback Service improvement must focus on increasing the efciency, maximizing the effectiveness and optimising the toll ofservices and the underlying Information technology service management processes. The just way to do this is to ensure that improvementopportunities are identied throughout the entire service lifecycle.The main purpose of Continual Service Improvement (CSI) is to continually align and re-align IT services to thechanging business needs by identifying and implementing improvements to It services that support businessprocesses. CSI looks for means to improve process effectiveness, efficiency and toll effectiveness. Other objectives include:
- Review, analyse and make recommendations on improvement opportunities in each lifecycle stage:
- Service strategy
- Service design
- Service transition
- Service operation
- and CSI itself!
- Identify and implement individual activities to meliorate Information technology service quality and improve the efficiency andeffectiveness of enabling ITSM processes
- Improve cost effectiveness of delivering IT services without sacrificing client satisfaction
- Ensure applicable quality management method is used
The Scope of Continual Service Improvement [5] The CSI Implementation process may vary and the correct way to implement it rely upon the arrangement's goal; it may be long term goals or brusque time dependent on the nature and policy of the organization. By and large the telescopic looks into three areas of ITSM.
- ITSM Processes
- IT Services
- The Service Lifecycle
Cartlidge & Lillycrop(2007) thinks it is very hard to decide from where to commencement, simply 1 of the above three areas can be taken as a starting point. Case ITIL (2006) suggests the organizations to address the hurting points first for getting value of Investment (VOI) too as gaining the business organization and functional grouping support. Example (2009) opines some quick wins similar low hanging fruits can be experienced during the implementing process.
- ITSM Processes- Where Practice we start?: Organizations are not enlightened of from where to offset the implementation of CSI in business. They can approach through change management, Incident Management and problem management by going into mature documenting process. Case (2009) argues change management as a control procedure and helps in attaining a maturity level for organizations protecting the production surroundings with the efficiency and effectiveness the process requires. Request for Modify (RFC) tin be a quick win if one doesn‟t be, or change advisory board highlighting the possible changes, procedures to implement changes, creating risk models and so forth.
- It Services- Where do nosotros start? Example (2009) states that it is crucial to cull right It services once the ITSM process is implemented in our business organization, to ensure the business value is delivered. But the problem is to identify the correct services but tin be simply done through identifying the services falling out to meet the satisfaction levels or which are continuously giving a threat. In instance of absenteeism of service level data a discussion is to be carried on with the business highlighting the services that are accounted mission critical. Bear upon assessment is to be conducted either to give continuity to the service or discard the service.
- Service lifecycle-where do nosotros start ? Starting the improvement initiatives of processes arrangement volition notice our many turning points for making improvements in the service lifecycle itself. Thus it is crucial that organisation keeps tracks of the advice and feedbacks betwixt different service lifecycle phases. Organizations should expect for improvement opportunities associated with the business concern requirements Example (2009) and Nickols (2010).
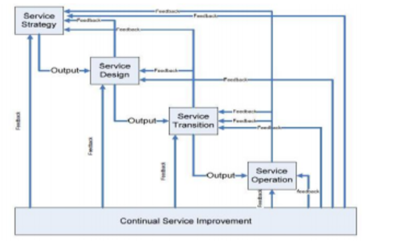
Ongoing feedback loop in CSI Service Levels
Processes of ITIL Continual Service Improvement (CSI)[6]
Every bit per ITIL v3, the following are the Four Main Processes of ITIL CSI process group, and the image below illustrates how they conformed to the 7-steps of Continual Service Improvement.
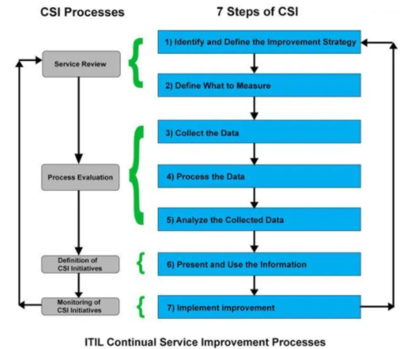
- Service Review: Responsible for reviewing business and infrastructure services on a regular basis. The aim of this process is to identify opportunity areas and search for more than economical ways of offer services.
- Process Evaluation: Responsible for evaluating processes on a regular basis to identifying areas where the targeted process metrics are not met. It also performs some regular tasks, such every bit benchmarking, audits, and reviews.
- Definition of CSI Initiatives: Used to define specific initiatives aimed to improve the quality of services and processes. The steps are planned based on the results of service reviews and process evaluations.
- Monitoring of CSI Initiatives: Used as a manner to verify if the improvement initiatives are proceeding according to the program and to introduce cosmetic measures if required.
See Too
References
- ↑ What is ITIL Continual Service Improvement (CSI)? Cerguidance
- ↑ CSI Model - ITIL Continual Service Improvement (CSI) Approach Pink Elephant
- ↑ The Seven Footstep Improvement Process of ITIL CSI [https://www.invensislearning.com/manufactures/itil/overview- of-itil-csi-and-the-7-step-improvement-process invensis]
- ↑ The Activities of Continual Service Comeback UCISA
- ↑ Telescopic of Continual Service Improvement Nabin Lamichhane
- ↑ Processes of ITIL Continual Service Improvement (CSI) Certguidance
Source: https://cio-wiki.org/wiki/ITIL_Continual_Service_Improvement_%28CSI%29
Posted by: meyerbesperstoont.blogspot.com


0 Response to "What Is The Process Within Continual Service Improvement?"
Post a Comment